As Seen In
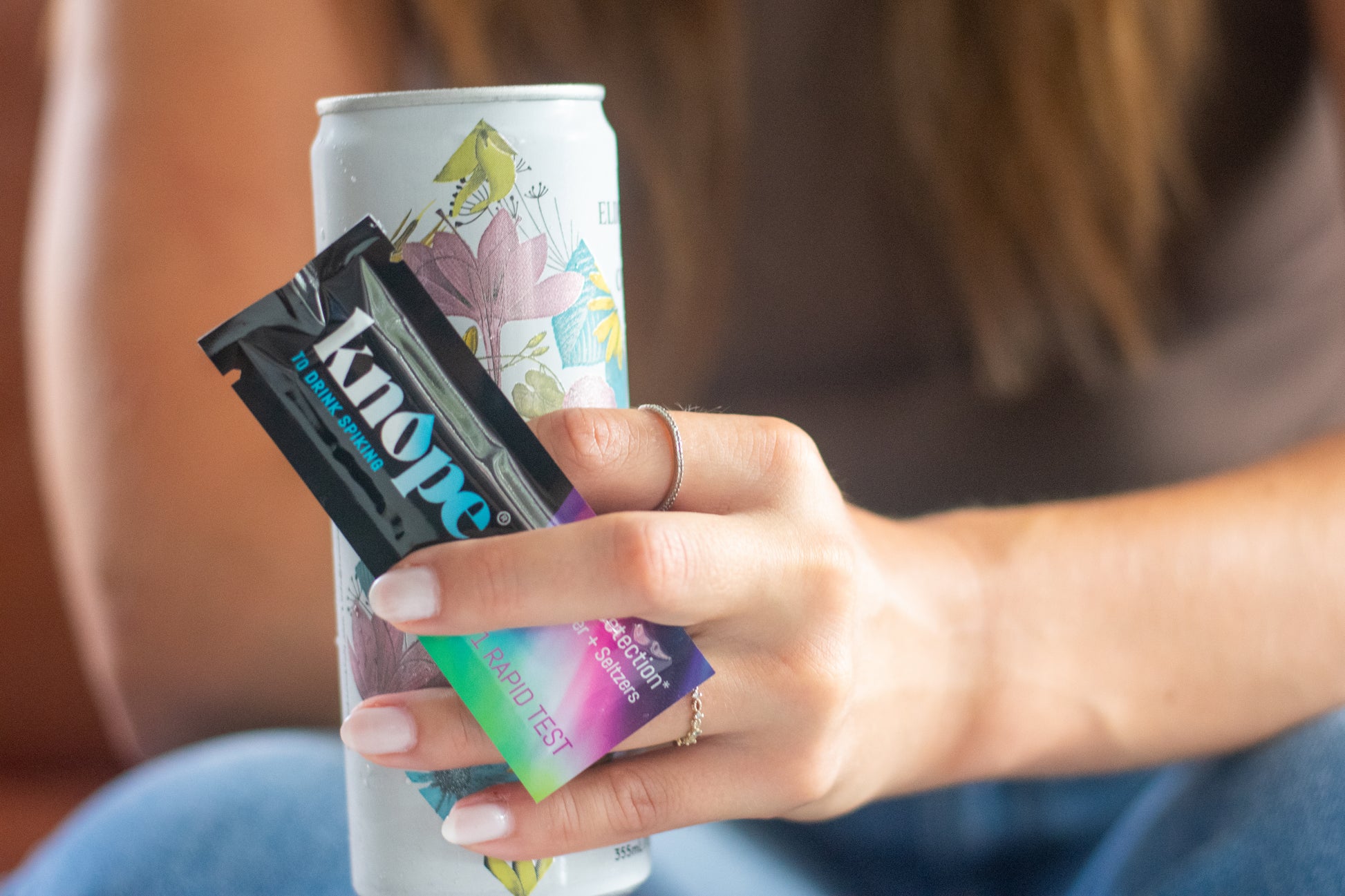
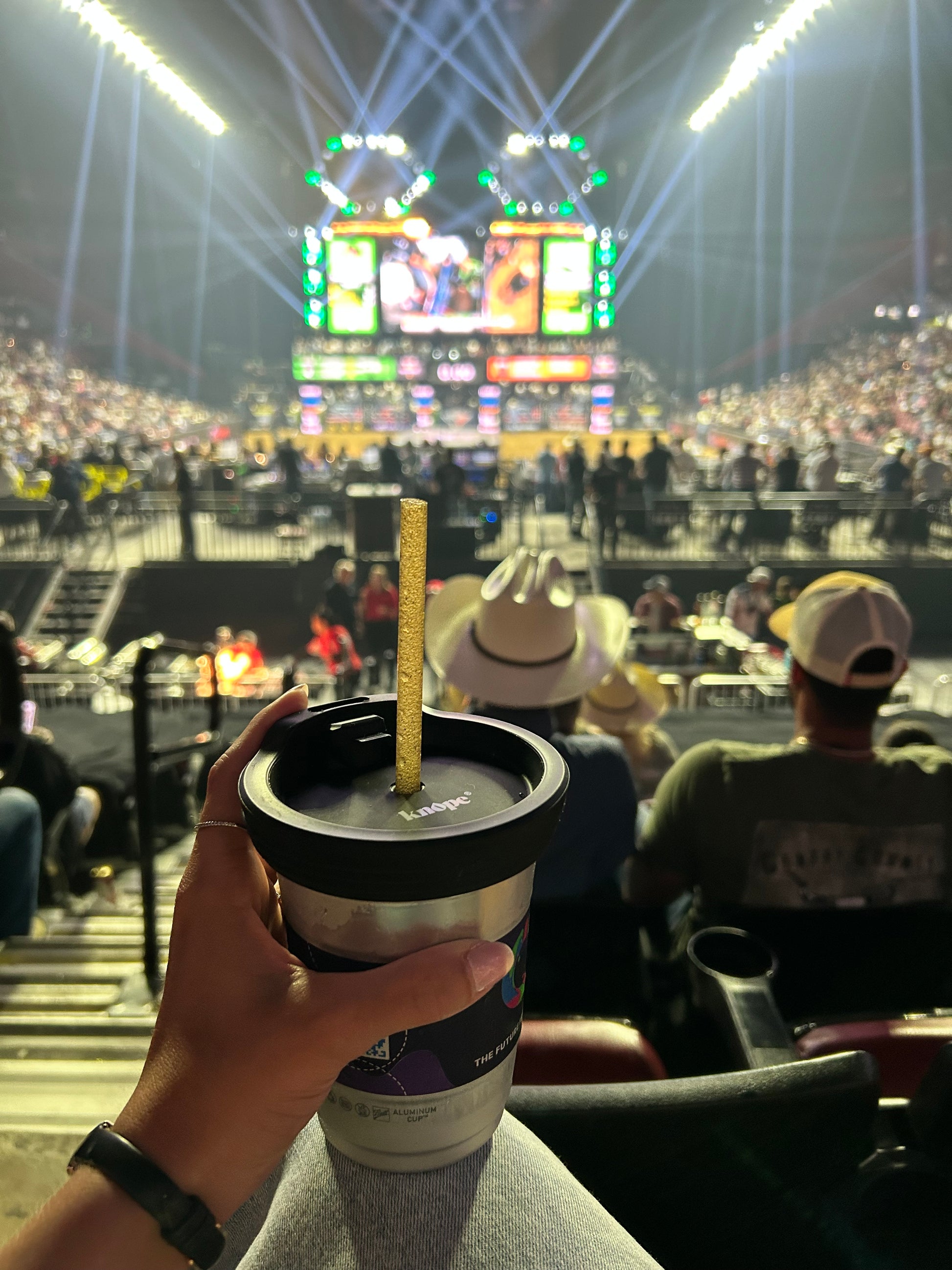
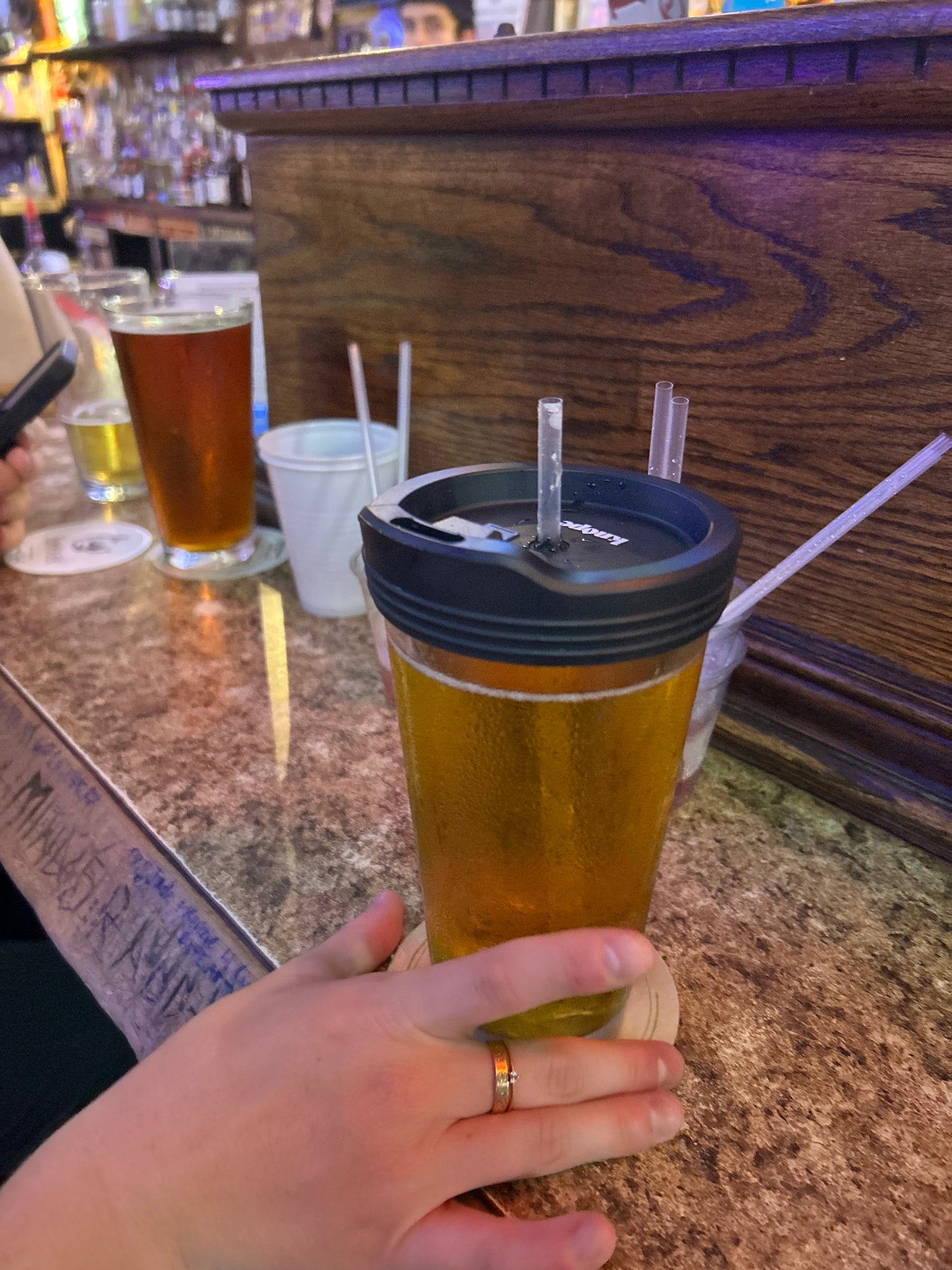
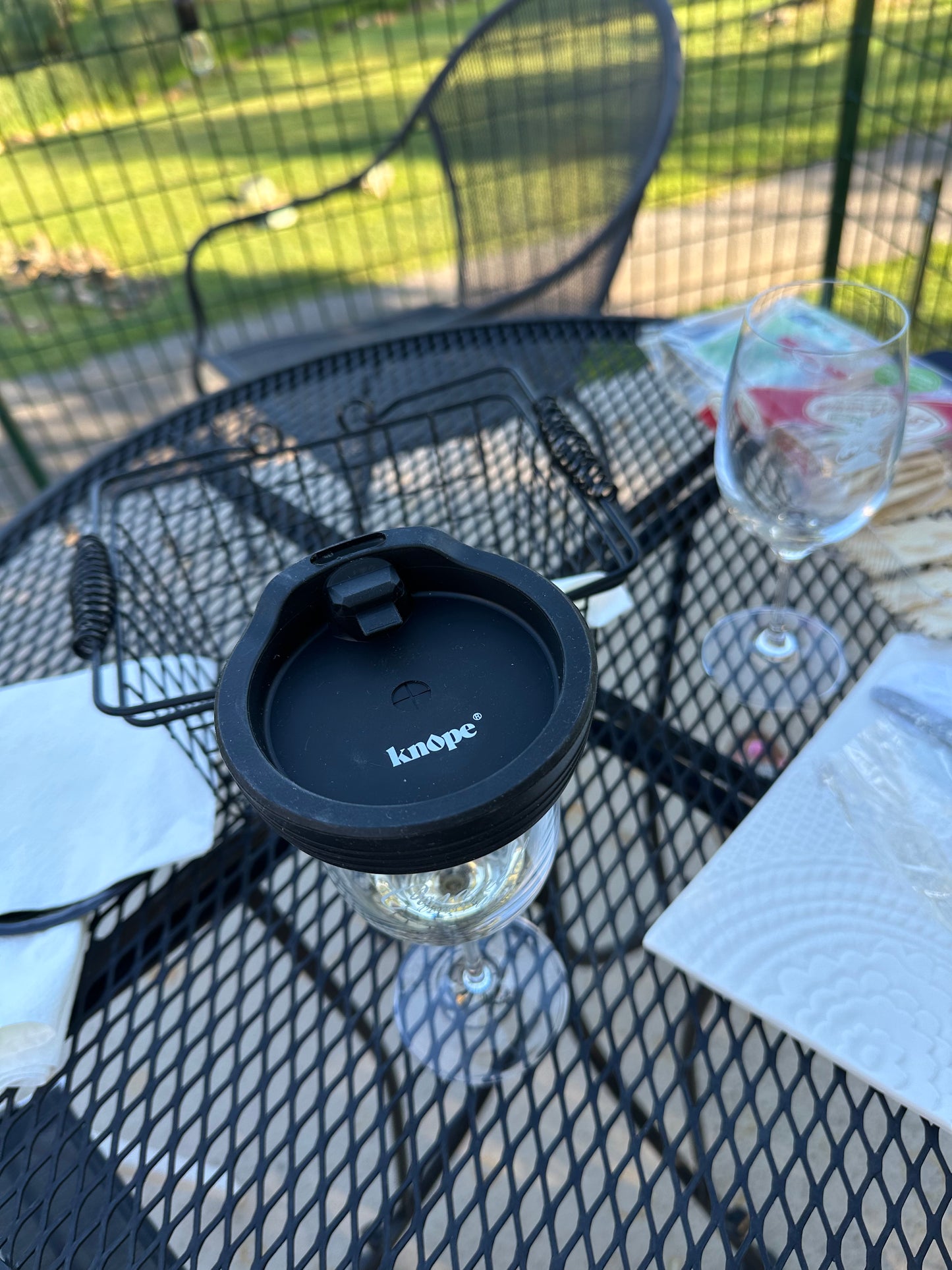
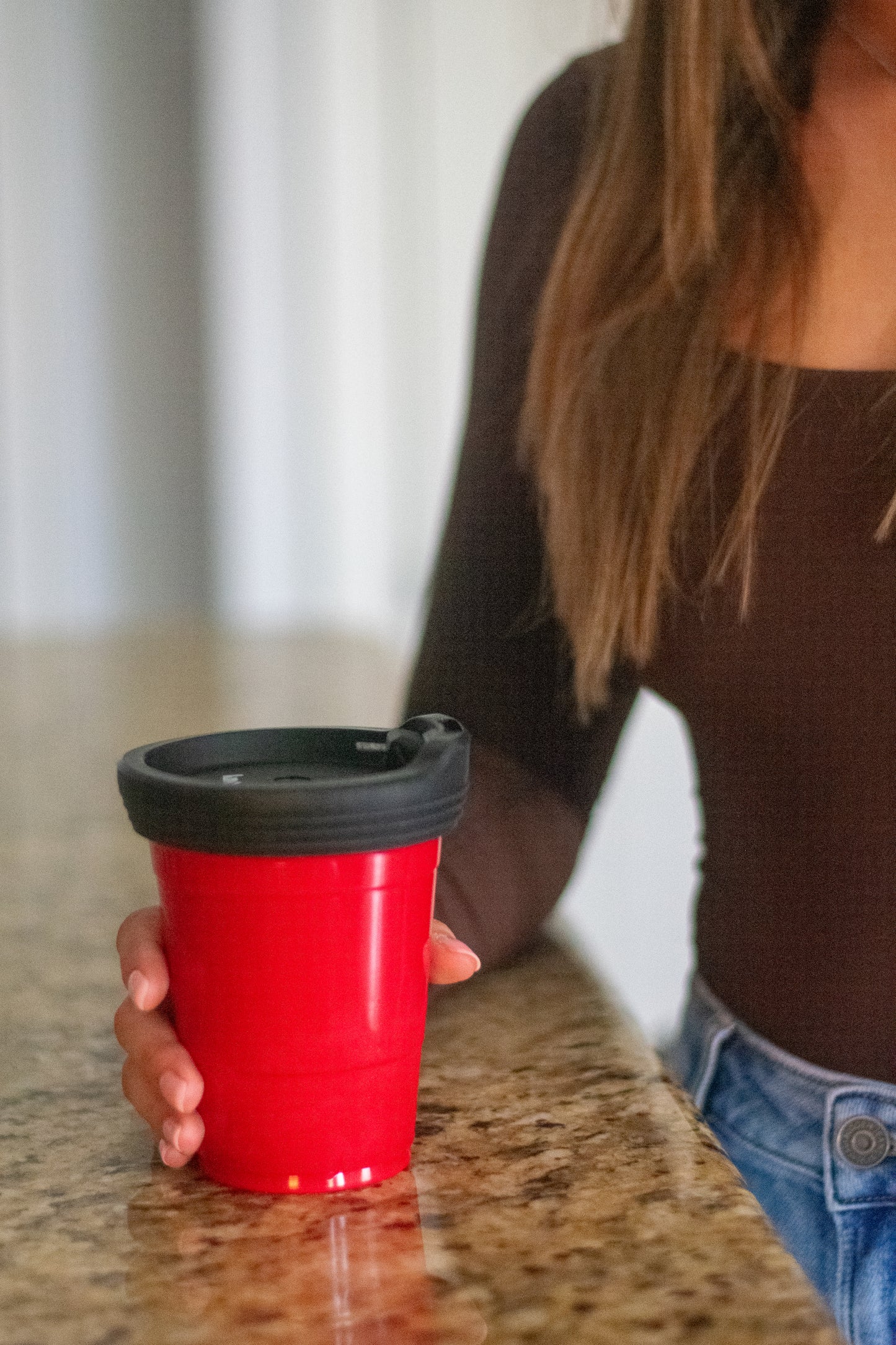
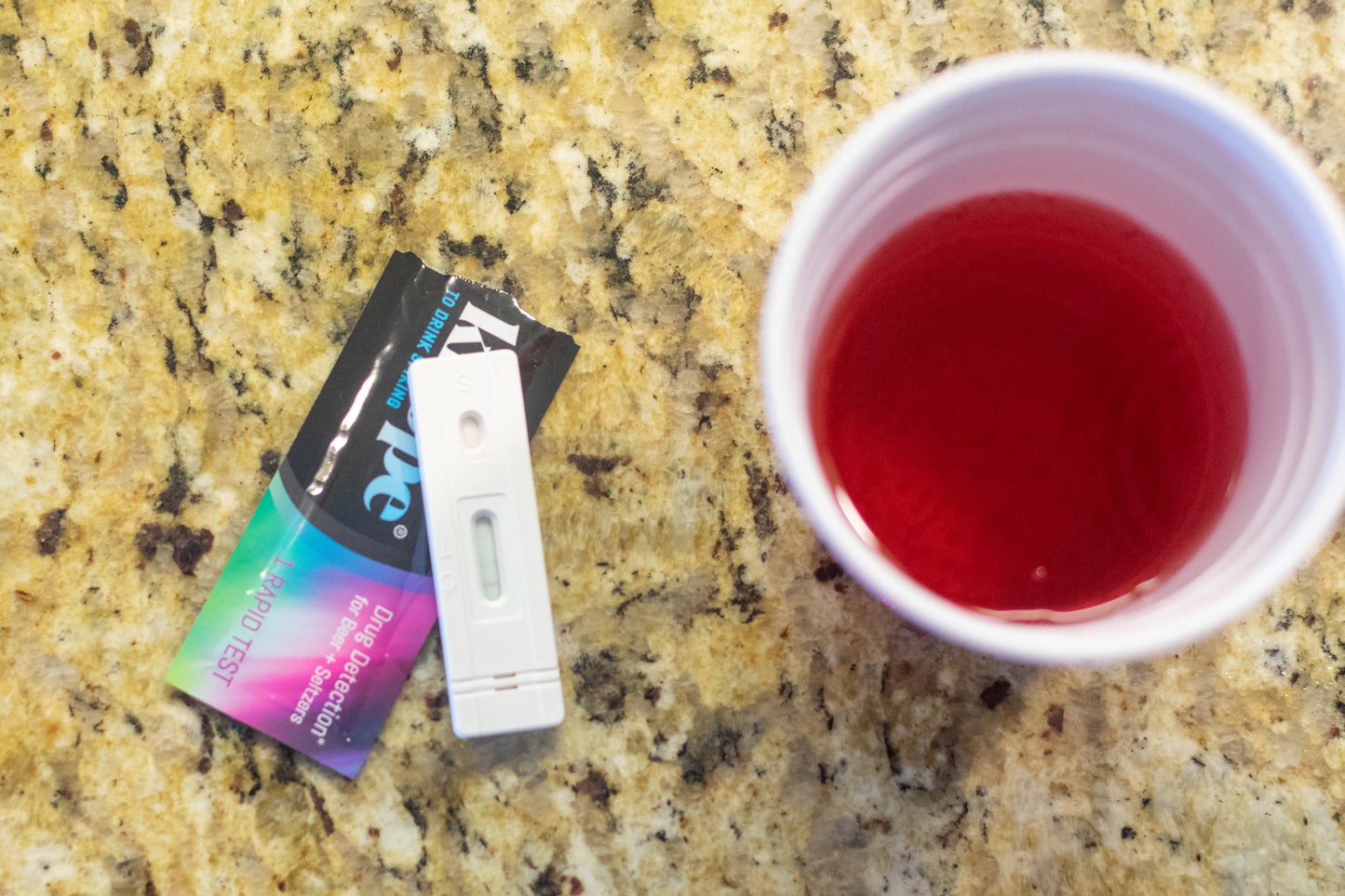
















12 Drugs Tested
Why test for Roofies?
Roofies, also commonly known as Rohypnol and scientifically known as Flunitrazepam, are a central nervous system (CNS) depressant. CNS depressants slow brain activity. This one produces sedative-hypnotic, anti-anxiety, and muscle relaxant effects.
When ingested, Roofies may cause drowsiness, a drop in blood pressure, memory loss, and loss of consiousness. It comes in pill form, easily dissolves in liquids, and is nearly impossible to detect by taste or smell.
Source CloseWhy test for Ketamine?
Ketamine, also commonly known as ‘K’ or ‘Special K’, is a dissociative anesthetic hallucinogen. After consumption, Ketamine makes the consumer feel detached from their environment, produces hallucinations, and distorts sight and sound for the consumer. Ketamine is frequently used as a party drug in combination with other substances.
Ketamine can induce sedation, immobility, pain relief, amnesia, distortion of sight and sound, and hallucinations. It frequently comes in liquid and powder form that dissolve easily in liquids.
Source CloseWhy test for Alprazolam?
Alprazolam is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant in the Benzodiazepine class. As a CNS, Alprazolam slows brain activity. It is used to treat anxiety and panic disorders. One example of Alprazolam is Xanax®.
When ingested, Alprazolam can cause dizziness/lightheadedness, sleepiness, abdominal pain, nausea/vomiting, seizures, hallucinations, low blood pressure, and memory loss. Effects of Alprazolam can become very dangerous when combined with alcohol or opioid use. Alprazolam comes in pill form with various shapes and colors and is easily dissolved in liquids.
Source 1 Source 2 CloseWhy test for Diazepam?
Diazepam is in the Benzodiazepine class. It is used to treat anxiety, seizures, muscle spasms and twitches. Diazepam is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant which slows brain activity. One example of Diazepam is Valium®.
When ingested, Diazepam may cause slow or shallow breathing, dizziness, confusion, and drowsiness/inability to stay awake. These symptoms can be exaggerated when consumed in connection with alcohol. Diazepam comes in the form of a tablet or liquid, and mixes easily in liquid.
Source 1 Source 2 CloseWhy test for Diastat?
Diastat is in the Benzodiazepine class. It is used to treat onset seizures. It is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant that slows brain function and activity.
When ingested, Diastat may cause drowsiness, dizziness, unsteadiness, hallucinations, and trouble speaking or walking. Consumption of Diastat with alcohol may increase dizziness and drowsiness.
Source 1 Source 2 CloseWhy test for Etizolam?
Etizolam is a chemical relative of Benzodiazepines. It is not approved for use in the United States but is used in Japan for neurological conditions like anxiety and insomnia. It has central nervous system (CNS) depressant effects that slow brain function and activity.
When ingested, Etizolam can cause strong hallucinations, drowsiness, sedation, muscle weakness, incoordination, confusion, slurred speech, and fainting. Etizolam comes in powder or tablet form, but has also been recently found on blotting paper.
Source CloseWhy test for Temazepam?
Temazepam is in the Benzodiazepine class. It is clinically used to treat insomnia as it helps you fall asleep faster, stay asleep, and wake up less often throughout the night. It is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant causing lower than normal brain activity. One example of Temazepam is Restoril®.
When ingested, Temazepam may cause short-term memory loss, dizziness, drowsiness, hallucinations, and confusion. Temazepam comes in capsule form that dissolves slightly in water and dissolves moderately in alcohol.
Source 1 Source 2 CloseWhy test for Norketamine?
Norketamine is a metabolic product of Ketamine. Your body breaks down Ketamine into Norketamine after consumption. Norketamine can also be made outside of the body. Being a dissociative drug, it can distort your senses and feelings.
When ingested, Norketamine can cause disorientation, loss of coordination, dizziness, nausea/vomiting, increased blood pressure and heart rate, and hallucinations. Norketamine can come in powder and liquid form.
Source 1 Source 2 CloseWhy test for Oxazepam
Oxazepam is in the Benzodiazepine class. It is usually used to treat anxiety and alcohol withdrawal as it is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant that decreases brain activity. One example of Oxazepam is Serax®.
When ingested, Oxazepam can cause drowsiness, dizziness, impaired vision, headaches, clumsiness, fainting, unusual tiredness, and trouble walking. Oxazepam is commonly distributed in tablet form that is easily dissolvable in water.
Source CloseWhy test for Nitrazepam?
Nitrazepam is in the Benzodiazepine class. It is commonly used to treat sleeping problems, such as insomnia. Nitrazepam is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant so it slows brain activity. One example is Mogadon®.
When ingested, Nitrazepam can cause drowsiness, dizziness, tiredness, confusion, clumsiness, memory loss, slurred speech, double visions, and difficulty breathing. It commonly comes in tablet form and is dissolvable in alcohol but not water.
Source 1 Source 2 CloseWhy test for Lorazepam?
Lorazepam is in the Benzodiazepine class. It is commonly used to treat anxiety. It is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant so it decreases brain activity. One example is Ativan®.
When ingested, Lorazepam can cause drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, impaired vision, loss of coordination, memory loss, and hallucinations. Lorazepam comes in oral tablet or liquid form, both are easily dissolvable in liquids.
Source 1 Source 2 CloseWhy test for Triazolam?
Triazolam is in the Benzodiazepine class. It is used to treat insomnia and is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant so it decreases brain function and activity. One example is Halcion®.
When ingested, Triazolam can cause dizziness, difficulty with coordination, drowsiness, memory loss, confusions, and hallucinations. It comes in tablet or powder form that is dissolvable in alcohol and not very dissolvable in water.
Source 1 Source 2 Close











